Bailey, Maya, Theo and Sam presented at TIPS!
📢 Excited to share that Bailey, Maya, Theo, and Sam presented at the 2025 Technology in Psychiatry Summit (TIPS)! 📝
Bailey
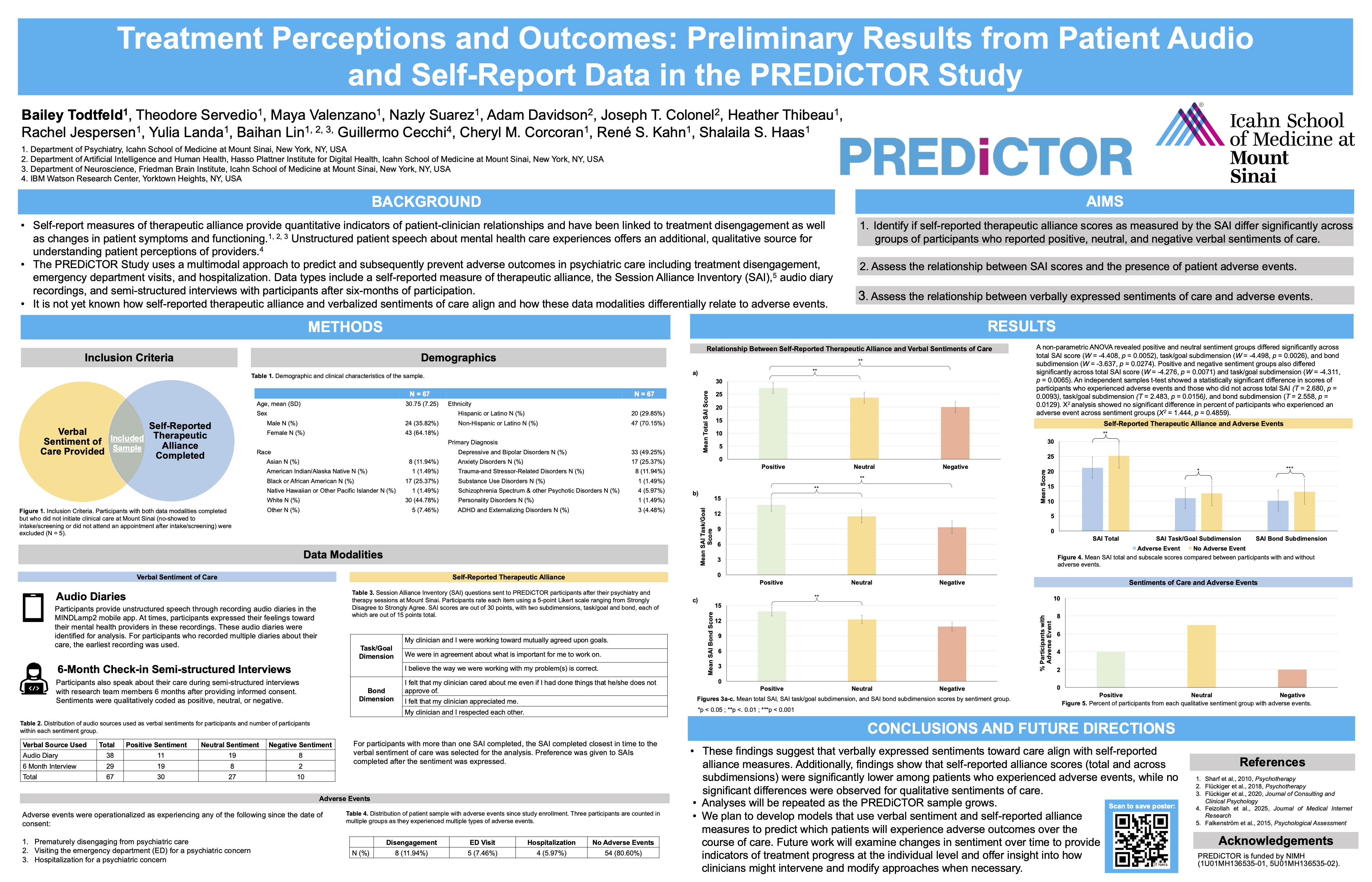
Bailey presented her work on “Treatment Perceptions and Outcomes: Preliminary Results from Patient Audio and Self-Report Data in the PREDiCTOR Study,” examining how patient audio data compares to traditional self-report measures within the PREDICTOR study. We analyzed the relationship between self-reported therapeutic alliance and verbally expressed sentiments of care to better understand treatment outcomes.
💡 Highlights:
1️⃣ We found that verbally expressed sentiments toward care aligned significantly with self-reported therapeutic alliance scores, validating the utility of unstructured audio data.
2️⃣ Patients who experienced adverse events (such as hospitalization or treatment disengagement) had significantly lower self-reported alliance scores compared to those who did not.
3️⃣ Interestingly, while self-reported scores were strong indicators of adverse events, the qualitative verbal sentiments did not show a statistically significant difference in this preliminary sample.
🚀 These findings suggest that while verbal feedback aligns with survey data, traditional self-reported alliance measures may offer a more sensitive signal early in the course of treatment for predicting adverse clinical outcomes.
Maya
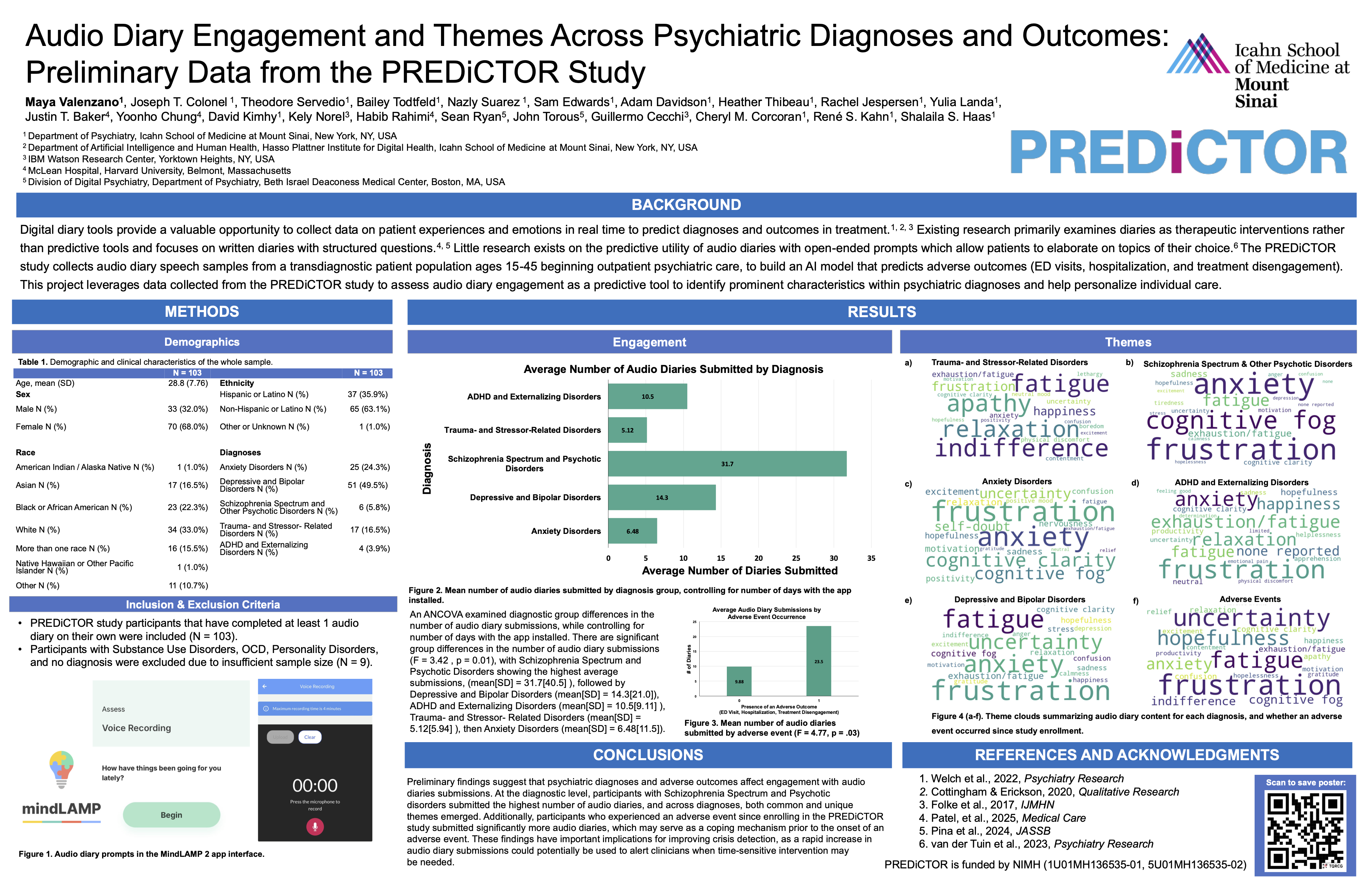
Maya presented her work on “Audio Diary Engagement and Themes Across Psychiatric Diagnoses and Outcomes: Preliminary Data from the PREDiCTOR Study”, using audio diary engagement as a predictive tool within the PREDICTOR study. By analyzing unstructured speech, we assessed how psychiatric diagnoses and adverse outcomes influence patient engagement with digital tools.
💡 Highlights:
1️⃣ We analyzed engagement across diverse diagnostic groups, finding that participants with Schizophrenia Spectrum disorders submitted the highest average number of diaries (31.7), followed by Depressive/Bipolar disorders.
2️⃣ Our analysis revealed that participants who experienced an adverse event (like hospitalization or ED visits) submitted significantly more audio diaries than those who did not.
3️⃣ Qualitative analysis uncovered unique themes for different diagnoses, such as “cognitive fog” in depression and “frustration/fatigue” in trauma-related disorders.
🚀 These findings suggest that rapid increases in audio diary submissions could serve as a digital biomarker, alerting clinicians when time-sensitive intervention is needed.
Sam
Sam presented his work comparing raw morphometry against normative modeling deviations for studying Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) and Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI). We utilized a robust model of brain morphometry developed in over 37,000 healthyindividuals to establish normative benchmarks.
💡 Highlights:
1️⃣ We found that normative deviations provided greater sensitivity than raw data in detecting disease-related brain changes, particularly in the hippocampus and amygdala.
2️⃣ The Z-score approach achieved a superior classification accuracy of 88.8% when distinguishing between AD and cognitively unimpaired individuals, compared to 79.5% for raw data.
3️⃣ The hippocampus stood out as the most prominent identifying feature in both models, while the amygdala was a prominent feature specifically in the Z-score model.
🚀 These results highlight normative modeling as a powerful framework for identifying sensitive biomarkers, advancing the field toward more precise, individualized diagnostics.

Theo
Theo presented his pilot study on optimizing audiovisual (AV) recording equipment for AI-driven psychiatric research. We evaluated the feasibility, patient comfort, and technical quality of various recording setups in real-world outpatient clinics.
💡 Highlights:
1️⃣ We tested five different setups, including single/dual iPhones and webcams, discovering that the OBSBOT webcam was rated as the most comfortable and least distracting by patients.
2️⃣ Visual quality control metrics showed that webcams and the single iPhone setup met or surpassed thresholds for high-quality facial analysis.
3️⃣ Patient acceptance was incredibly high, with 93.5% of participants willing to consent to their clinical settings being recorded using the OBSBOT setup.
🚀 This study confirms that minimally invasive webcams are a feasible solution for integrating objective behavioral data collection into standard psychiatric care.